Author's: Kh. Roumaih and M. Kaiser
Pages: [159] - [171]
Received Date: November 16, 2009
Submitted by: Kin Ho Lo
The effect of gallium substitution on conduction mechanism and the
magnetic properties of 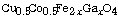 ferrites have been studied. It was found that
the value of the DC electrical conductivity decreased with the
increasing of
ferrites have been studied. It was found that
the value of the DC electrical conductivity decreased with the
increasing of 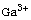 concentration. The thermoelectric power
concentration. The thermoelectric power
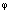 is negative, which indicates n-type
semiconductor behavior for all samples. The hysteresis curve recorded
at room temperature shows that the samples are ferrimagnetic at room
temperature. The coercive field
is negative, which indicates n-type
semiconductor behavior for all samples. The hysteresis curve recorded
at room temperature shows that the samples are ferrimagnetic at room
temperature. The coercive field 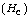 decreases with increasing
decreases with increasing 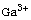 content in the samples, indicating that the
loss of magneto crystalline anisotropy. The initial permeability
content in the samples, indicating that the
loss of magneto crystalline anisotropy. The initial permeability
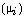 is steadily decreased with the increasing
temperature and becomes constant at a very small value of
is steadily decreased with the increasing
temperature and becomes constant at a very small value of 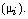 The Curie temperature decreases with
increasing
The Curie temperature decreases with
increasing 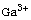 concentration.
concentration.
conduction mechanism, magnetic properties, thermoelectric power, ferrimagnetic ferrites.