Author's: Ryuta Iba, Yuki Adachi, Ariyuki Kato, Koichiro Oishi, Hironori Katagiri and Kanji Yasui
Pages: [29] - [41]
Received Date: March 26, 2019
Submitted by:
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18642/jmseat_7100122042
Nitrogen doping of ZnO films by the decomposition of NO gas using a
heated Ir wire during film growth was attempted through the reaction
between dimethylzinc (DMZn) and high-temperature 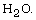 High-temperature
High-temperature 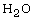 was produced by the Pt-catalyzed reaction
between
was produced by the Pt-catalyzed reaction
between 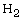 and
and 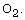 Although p-type ZnO films were not obtained,
the residual carrier concentration decreased upon the addition of NO
gas. In X-ray photoelectron spectra, multiple overlapping N-1s peaks
were observed from 395eV to 408eV. By deconvoluting the spectra,
components such as Zn-N, N-H, N-N, and
Although p-type ZnO films were not obtained,
the residual carrier concentration decreased upon the addition of NO
gas. In X-ray photoelectron spectra, multiple overlapping N-1s peaks
were observed from 395eV to 408eV. By deconvoluting the spectra,
components such as Zn-N, N-H, N-N, and 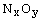 were identified. The relative intensity of the
Zn-N peak at 395.5eV-396.8eV increased when a heated Ir wire was used
to decompose the NO gas.
were identified. The relative intensity of the
Zn-N peak at 395.5eV-396.8eV increased when a heated Ir wire was used
to decompose the NO gas.
ZnO, catalytic reaction, Ir hot-wire, nitrogen doping.