Author's: Gustavo Castro-Sánchez, Christian I. Otero-Vázquez and José Lemus-Ruiz
Pages: [1] - [16]
Received Date: March 16, 2017
Submitted by:
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18642/jmseat_7100121800
The main objective of this work was to study various aspects of liquid
state diffusion bonding of cylindrical samples of WC (with 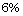 Co) and commercially pure super alloy
Inconel 600 produced by brazing using a 25μm thick 70Cu-30Zn
Co) and commercially pure super alloy
Inconel 600 produced by brazing using a 25μm thick 70Cu-30Zn
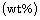 alloy as joining element. Joining
experiments were carried out on WC/Cu-Zn/Inconel 600 combinations at
temperature of 980°C and 1000°C using different holding times
under argon (Ar) atmosphere. The results show that it is possible
create a successful joint at temperature and times used and joining
occurred by the formation of a diffusion zone. The joining is feasible
because it presents an homogeneous interface with no several
interfacial cracking and porosity. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
micrographs show the different intermediate diffusion layers formed in
the reaction zone, and the width of these layers increases with
bonding temperature and time. Electron probe microanalysis (EPMA)
revealed that at any particular bonding temperature, Co of the WC, as
well as Ni, Cr, and Fe of the Inconel 600, travels into the Cu-Zn
joining elements. Some points of precipitation of Cr are observed in
both, close the WC and the Inconel 600 of the interface. Joining
strength was obtained by shear testing with a maximum joint strength
of 44MPa for WC/Cu-Zn/Inconel 600 samples joined at 1000°C and 25
minutes.
alloy as joining element. Joining
experiments were carried out on WC/Cu-Zn/Inconel 600 combinations at
temperature of 980°C and 1000°C using different holding times
under argon (Ar) atmosphere. The results show that it is possible
create a successful joint at temperature and times used and joining
occurred by the formation of a diffusion zone. The joining is feasible
because it presents an homogeneous interface with no several
interfacial cracking and porosity. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
micrographs show the different intermediate diffusion layers formed in
the reaction zone, and the width of these layers increases with
bonding temperature and time. Electron probe microanalysis (EPMA)
revealed that at any particular bonding temperature, Co of the WC, as
well as Ni, Cr, and Fe of the Inconel 600, travels into the Cu-Zn
joining elements. Some points of precipitation of Cr are observed in
both, close the WC and the Inconel 600 of the interface. Joining
strength was obtained by shear testing with a maximum joint strength
of 44MPa for WC/Cu-Zn/Inconel 600 samples joined at 1000°C and 25
minutes.
WC, inconel 600, diffusion bonding, Cu-Zn alloy, sheer strength.