Author's: A. M. Aksenczuk, A. Calka and D. Wexler
Pages: [77] - [104]
Received Date: March 3, 2017
Submitted by:
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18642/jmseat_7100121815
This paper describes a novel mixing method together with mixing
device. The Micro Pulse Mixer 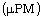 has been designed, constructed and tested
using a new mixing concept based on damped harmonic oscillator motion.
Advantages of the technique include simplicity of the device, high
rates of mixing and high uniformity of product. Furthermore, the
device design, with discrete powder containers, allows rapid loading
and unloading of samples
has been designed, constructed and tested
using a new mixing concept based on damped harmonic oscillator motion.
Advantages of the technique include simplicity of the device, high
rates of mixing and high uniformity of product. Furthermore, the
device design, with discrete powder containers, allows rapid loading
and unloading of samples  enabling powder sampling and/or complex
blending operations. The mixer does not require frequent cleaning. It
is designed to mix relatively small volumes of powders (up to several
grams) for use in either laboratory work or for small commercial
samples of high value.
enabling powder sampling and/or complex
blending operations. The mixer does not require frequent cleaning. It
is designed to mix relatively small volumes of powders (up to several
grams) for use in either laboratory work or for small commercial
samples of high value.
In this study we compared the 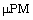 method with rotating tumbling mixing.
Mixing products were evaluated by analysis of scanning electron
microscope (SEM) images while X-ray diffraction (XRD) was used to
monitor phase evolution during mixing. Powder particle distributions
were obtained based on image analysis techniques with mixing
efficiency parameters determined based on the calculation of the
percentage compounds content within sampled powder is proposed.
method with rotating tumbling mixing.
Mixing products were evaluated by analysis of scanning electron
microscope (SEM) images while X-ray diffraction (XRD) was used to
monitor phase evolution during mixing. Powder particle distributions
were obtained based on image analysis techniques with mixing
efficiency parameters determined based on the calculation of the
percentage compounds content within sampled powder is proposed.
We believe that the more efficient approach of impulse mixing could be
beneficial for laboratory purposes and as a simple and cost-effective
powder mixing and blending method.
powder mixing, pulse mixer, mixing mechanisms, deagglomeration, effective mixing coefficient.