[1] A. H. Landrock, Handbook of Plastic Foams: Types, Properties,
Manufacture and Applications, Elsevier Science, New York, 1995.
[2] A. Gardziella, L. A. Pilato and A. Knop, Phenolic Resins:
Chemistry, Applications, Standardization, Safety and Ecology,
Springer, Berlin, 2000.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-04101-7
[3] L. J. Gibson and M. F. Ashby, Cellular Solids: Structure and
Properties, Cambridge University Press, New York, 1999.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139878326
[4] L. Pilato, Phenolic Resins: A Century of Progress, Springer,
Berlin, 2010.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04714-5
[5] J. D. Carlson, V. J. Wojtyna, E. W. Kifer and J. P. Colton,
Phenolic Foam and Composition and Method for Preparing the Same,
CA1209749 A, August 12, 1986.
[6] M. C. Saha et al., Effect of density, microstructure, and strain
rate on compression behavior of polymeric foams, Materials Science and
Engineering: A 406(1-2) (2005), 328-336.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2005.07.006
[7] M. L. Auad et al., Flammability properties and mechanical
performance of epoxy modified phenolic foams, Journal of Applied
Polymer Science 104(3) (2007), 1399-1407.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.24405
[8] B. Del Saz-Orozco et al., Effects of formulation variables on
density, compressive mechanical properties and morphology of wood
flour-reinforced phenolic foams, Composites Part B: Engineering 56
(2014), 546-552.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.08.078
[9] A. Desai et al., Mechanical behavior of hybrid composite phenolic
foam, Journal of Cellular Plastics 44(1) (2008), 15-36.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0021955X07078021
[10] H. Shen, A. J. Lavoie and S. R. Nutt, Enhanced peel resistance of
fiber reinforced phenolic foams, Composites Part A: Applied Science
and Manufacturing 34(10) (2003), 941-948.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-835X(03)00210-0
[11] H. Shen and S. Nutt, Mechanical characterization of short fiber
reinforced phenolic foam, Composites Part A: Applied Science and
Manufacturing 34(9) (2003), 899-906.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-835X(03)00136-2
[12] Datasheet of Last-A-Foam 3700, Series - General Plastics,
Accessed 31 May 2018.
https://www.nrc.gov/docs/ML0504/ML050410066.pdf
[13] B. Del Saz-Orozco et al., Mechanical, thermal and morphological
characterization of cellulose fiber-reinforced phenolic foams,
Composites Part B: Engineering 75 (2015), 367-372.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.01.049
[14] B. Del Saz-Orozco et al., Lignin particle- and wood
flour-reinforced phenolic foams: Friability, thermal stability and
effect of hygrothermal aging on mechanical properties and morphology,
Composites Part B: Engineering 80 (2015), 154-161.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.05.043
[15] V. K. Rangari et al., Cloisite clay-infused phenolic foam
nanocomposites, Journal of Applied Polymer Science 103(1) (2007),
308-314.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.25287
[16] Q. Xu et al., Preparation of high-strength microporous phenolic
open-cell foams with physical foaming method, High Performance
Polymers 27(7) (2015), 852-867.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0954008314564197
[17] F. Saint-Michel et al., Mechanical properties of high density
polyurethane foams: I, Effect of the density, Composites Science and
Technology 66(15) (2006), 2700-2708.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2006.03.009
[18] Y. Chen, R. Das and M. Battley, Effects of cell size and cell
wall thickness variations on the stiffness of closed-cell foams,
International Journal of Solids and Structures 52 (2015), 150-164.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2014.09.022
[19] Z. G. Xu et al., Effects of cell size on quasi-static compressive
properties of Mg alloy foams, Materials & Design 34 (2012), 40-44.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.07.066
[20] C. Gaétane, Elaboration et Caractérisation de Matériaux
Polymères Poreux Modèles à Base d’Émulsions Contrôlées, in,
Université Sciences et Technologies - Bordeaux I, 2001.
[21] G. K. Rickle and K. R. Denslow, The effect of water on phenolic
foam cell structure, Journal of Cellular Plastics 24(1) (1988),
70-78.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0021955X8802400104
[22] R. Gosselin and D. Rodrigue, Cell morphology analysis of high
density polymer foams, Polymer Testing 24(8) (2005), 1027-1035.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2005.07.005
[23] W. E. Warren and A. M. Kraynik, The linear elastic properties of
open-cell foams, Journal of Applied Mechanics 55(2) (1988),
341-346.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3173680
[24] C. Yang, Z. H. Zhuang and Z. G. Yang, Pulverized polyurethane
foam particles reinforced rigid polyurethane foam and phenolic foam,
Journal of Applied Polymer Science 131(1) (2014), 39734.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.39734
[25] H. Yu, L. Wang and G. Gai, Performance of modified aramid fiber
reinforced phenolic foam, Advanced Materials Research 557-559 (2012),
258-261.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.557-559.258
[26] J. J. Yuan, Y. B. Zhang and Z. Z. Wang, Phenolic foams toughened
with crosslinked poly (n-butyl acrylate)/silica core-shell
nanocomposite particles, Journal of Applied Polymer Science 132(40)
(2015), 42590.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.42590
[27] L. Li et al., Preparation and characterization of phenolic foam
modified by Nitrile butadiene rubber powder, Applied Mechanics and
Materials 204-208 (2012), 4137-4142.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.204-208.4137
[28] Y. Ma et al., Effect of zinc oxide on properties of phenolic
foams/halogen-free flame retardant system, Journal of Applied Polymer
Science 132(44) (2015), 42730.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.42730
[29] Q. Li et al., Effect of nano-titanium nitride on thermal
insulating and flame-retardant performances of phenolic foam, Journal
of Applied Polymer Science 133(32) (2016), 43765.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.43765
[30] X. Li et al., One-step in situ synthesis of a novel
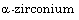 phosphate/graphene oxide hybrid and its
application in phenolic foam with enhanced mechanical strength, flame
retardancy and thermal stability, RSC Advances 6(78) (2016),
74903-74912.
phosphate/graphene oxide hybrid and its
application in phenolic foam with enhanced mechanical strength, flame
retardancy and thermal stability, RSC Advances 6(78) (2016),
74903-74912.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA12208F
[31] Y. F. Yang and J. M. He, Mechanical characterization of phenolic
foams modified by short glass fibers and polyurethane prepolymer,
Polymer Composites 36(9) (2015), 1584-1589.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.23066
[32] H. Y. Ding et al., Preparation and properties of a novel flame
retardant polyurethane quasi-prepolymer for toughening phenolic foam,
Journal of Applied Polymer Science 132(35) (2015), 42424.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.42424
[33] J. T. Zhou et al., Fabrication and mechanical properties of
phenolic foam reinforced with graphene oxide, Polymer Composites 35(3)
(2014), 581-586.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.22698