[1] S. H. Avner, Introducción a la metalurgia física, Segunda
Edición McGrawhill, México D.F., 1994.
[2] J. Colnet, E. Pirard, J. Lecomte-Beckers, P. Boeraeve and R.
Ghfiri, Quantitative description of 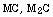 and
and 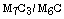 carbides in high speed steel rolls, Tchoufang
– Proceedings of MSMF-3 International Conference, Brno, Czech
Republic (2001), 710-717.
carbides in high speed steel rolls, Tchoufang
– Proceedings of MSMF-3 International Conference, Brno, Czech
Republic (2001), 710-717.
[3] Keun Chul Hwang, Sunghak Lee and Hui Choon Lee, Effects of
alloying elements on microstructure and fracture properties of cast
high speed steel rolls: Part I: Microstructural analysis, Materials
Science and Engineering A, Elsevier Science SA 254(1-2) (1998),
282-295.
[4] K. K. Chang, J. Park, L. Sunghak and K. Y. Chan, Effects of
alloying elements on microstructure, hardness, and fracture toughness
of centrifugally cast high-speed steel rolls, Metallurgical and
Materials Transactions 36A (1) (2005), 87-97.
Doi:10.1007/s11661-005-0141-0
[5] Dae Jin Ha, Effects of alloying elements on microstructure,
hardness, wear resistance, and surface roughness of centrifugally cast
high-speed steel rolls, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A,
Korea 40A (2009), 2568-2577.
DOI: 10.1007/s11661-009-0006-z
[6] C. K. Kim, D.-G. Lee and S. Lee, Correlation of microstructure and
fracture properties of five centrifugal cast high speed steel rolls,
Materials Science and Technology 23(9) (2007), 1065-1074.
Doi:10.1179/174328407X213170
[7] Kim Chang Kyu; Park, Il Jong, Jae Hwa Ryu and Sunghak Lee,
Correlation of microstructure and thermal-fatigue properties of
centrifugally cast high-speed steel rolls, Metallurgical and Materials
Transactions A 35(2) (2004), 481-492.
Doi:10.1007/s11661-004-0359-2
[8] L. De Colnet, E. Pirard, J. Tchoufang Tchuindjang, J. Lecomte
Beckers, R. Gfhiri, P. Boeraeve and S. Cescotto, Quantitative
description of 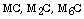 and
and 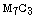 carbides in high speed steel rolls, University
of Liège, Liège, Belgium, In proceedings of the MSMF-3 international
conference held in Brno, Krakowic (2001), 710-717.
carbides in high speed steel rolls, University
of Liège, Liège, Belgium, In proceedings of the MSMF-3 international
conference held in Brno, Krakowic (2001), 710-717.
[9] J. W. Park, H. C. H. Lee and S. Lee, Composition, microstructure,
hardness, and wear properties of high-speed steel rolls, Metallurgical
and Materials Transactions A, Korea 30A (1999), 399-409.
Doi:10.1007/s11661-999-0329-9
[10] J. Blaha, C. Krempaszky and E. A. Werner, Carbide distribution
effects in cold work tool steels, Proceedings of the 6th International
Tooling Conference, Karlstad, Sweden, Karlstad University (2002),
289-298.
[11] M. Boccalini Jr. and A. Sinatora, Microstructure and wear
resistance of high speed steel for rolling mills rolls, Proceedings of
the 6th International Tooling Conference, Karlstad, Sweden, Karlstad
University (2002), 509-524.
[12] C. Rodenburg and W. M. Rainforth, A quantitative analysis of the
influence of carbides size distributions on wear behaviour of
high-speed steel in dry rolling/sliding contact, Elsevier Ltd.,
IMMPETUS, Department of Engineering Materials, University of
Sheffield, Acta Materialia 55 (2007), 2443-2454.
Doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2006.11.039
[13] K. L. Johnson, Contact Mechanics, Cambridge University Press,
Cambridge, 1985.
[14] W. Sitek, A mathematical model of the hardness of high-speed
steels, Transactions of Famena XXXIV-3, Institute of Engineering
Materials and Biomaterials Silesian University of Technology, Gliwice,
Poland (2010), 39-46. UDC 669.14:539.53
[15] ASTM E3-91, Standard practice for preparation of meta¬llographic
specimens, ASTM International (1991), 82-86.
[16] ASTM E92-82, Standard test methods for Vickers hardness of
metallic materials, ASTM International (1991), 260-268.
[17] ASTM E18-89a, Standard test methods for Rockwell hardness and
Rockwell superficial hardness of metallic materials, ASTM
International (1991), 176-189.