Author's: Moslem Mansour Lakouraj and Vahid Hasantabar
Pages: [39] - [58]
Received Date: August 8, 2019
Submitted by:
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18642/jmseat_7100122095
The development of simple methods for the removal of heavy metal
cations from water samples is an attractive field of research. In this
regard, two novel magnetic tri-layer core-shell-shell bioactive
nanocomposites, polypyrrole@polyxanthone 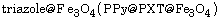 and polyaniline@polyxanthone triazole@
and polyaniline@polyxanthone triazole@
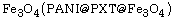 were prepared by a combination process
involving click reaction and emulsion polymerization, successfully.
Then, uptake of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from an aqueous solution by
introduced materials was evaluated as a function of pH, adsorption
dosage, contact time, and initial concentration of Pb(II) and Cd(II)
through batch studies. The bioactive nanocomposites exhibited a high
adsorption percentage 92.63 and 72.84 for Pb(II) and 90.66 and 93.70
for Cd(II) in optimized conditions, respectively.
were prepared by a combination process
involving click reaction and emulsion polymerization, successfully.
Then, uptake of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from an aqueous solution by
introduced materials was evaluated as a function of pH, adsorption
dosage, contact time, and initial concentration of Pb(II) and Cd(II)
through batch studies. The bioactive nanocomposites exhibited a high
adsorption percentage 92.63 and 72.84 for Pb(II) and 90.66 and 93.70
for Cd(II) in optimized conditions, respectively.
Isotherm and kinetic models showed that interactions of Pb(II) and
Cd(II) with bioactive nanocomposites were in good agreement with the
Freundlich isotherm and pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The maximum
adsorption capacity 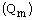 of Pb(II) for two bioactive nanocomposites was
313 and 526mg/g, and in about Cd(II) was found 357 and 555.5mg/g,
respectively. Hence, the introduced bioactive nanocomposites with high
efficiency can be promising candidates for microorganism deactivator
and risky ions removal in household water treatment.
of Pb(II) for two bioactive nanocomposites was
313 and 526mg/g, and in about Cd(II) was found 357 and 555.5mg/g,
respectively. Hence, the introduced bioactive nanocomposites with high
efficiency can be promising candidates for microorganism deactivator
and risky ions removal in household water treatment.
nanobioactive, ion removal, household water treatment, Pb(II), Cd(II).